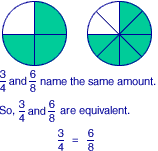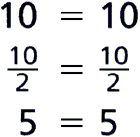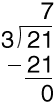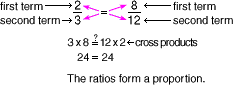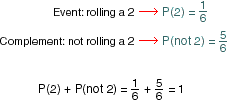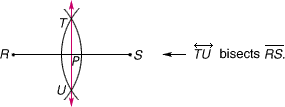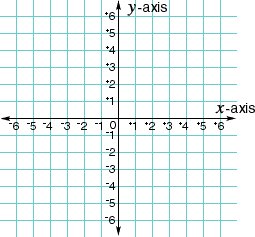Copy of `Harcourt school publishers - Math glossary`
The wordlist doesn't exist anymore, or, the website doesn't exist anymore. On this page you can find a copy of the original information. The information may have been taken offline because it is outdated.
|
|
|
Harcourt school publishers - Math glossary
Category: Mathematics and statistics
Date & country: 23/12/2007, UK
Words: 270
|
estimateTo find a number that is close to an exact amount
Example:
32 x 9


30 x 10 = 300

estimate
32 x 9 is about 300.
equivalent ratiosRatios that name the same comparisons
Example:
 equivalent fractions
equivalent fractionsFractions that name the same amount
Example:
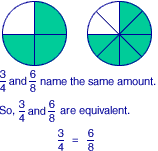 equivalent
equivalentHaving the same value
Examples:
These expressions are equivalent.
4 + 3 = 8 â€` 1
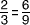 equivalent decimals
equivalent decimalsDecimals that name the same amount
Example:
0.5 = 0.50 = 0.500
equilateral triangleA triangle with three congruent sides
Example:
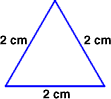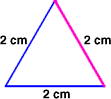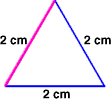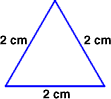 equation
equationAn algebraic or numerical sentence that shows that two quantities are equal
Examples:
3 + 7 = 10
4 â€` 1 = 3
12 + n = 21
equally likelyHaving the same chance of occuring
Example:

You are equally likely to roll 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, or 6.
edgeThe line segment where two faces of a solid figure meet
Example:
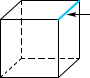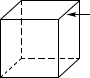
edge
divisorThe number that divides the dividend
Example:
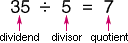
The divisor is 5.
Division Property of EqualityThe property that states that if you divide both sides of an equation by the same nonzero number, the sides remain equal
Example:
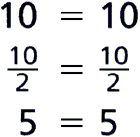 divisible
divisibleA number is divisible by another number if the quotient is a whole number and the remainder is zero
Example:
21 is divisible by 3.
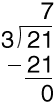 dividend
dividendThe number that is to be divided in a division problem
Example:
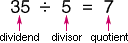
The dividend is 35.
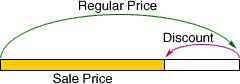
discountAn amount that is subtracted from the regular price of an item
Example:
 dimension
dimensionA measure in one direction; the length, width, or height of a figure
differenceThe answer in a subtraction problem
Example:
8
8 â€` 5 = 3 â€` 5
3 3 is the difference.
diameterA line segment that passes through the center of a circle and has its endpoints on the circle
Example:
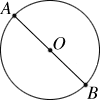
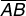
is a diameter of circle O.
dependent eventsEvents for which the outcome of the second event depends on the outcome of the first event
Example:
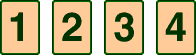
Drawing a card and not replacing it, and then drawing a second card are dependent events.
denominatorThe number below the bar in a fraction that tells how many equal parts are in the whole
Example:
 degree Fahrenheit (°F)
degree Fahrenheit (°F)A customary unit for measuring temperature
Example:
 degree Celsius (°C)
degree Celsius (°C)A metric unit for measuring temperature
Example:
 degree
degreeA unit for measuring angles and temperature
Examples:
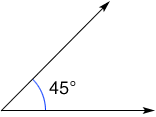
 decimal system
decimal systemA numeration system based on grouping by tens
Example:
 data
dataA set of information
decimalA number with one or more digits to the right of the decimal point
Example:
3.27
customary measurement systemA measurement system that measures length in inches, feet, yards, and miles; capacity in cups, pints, quarts, and gallons; weight in ounces, pounds, and tons; and temperature in degrees Fahrenheit
cylinderA solid figure with two parallel bases that are congruent circles
Examples:

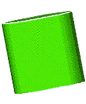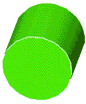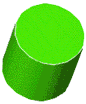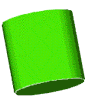 cumulative frequency
cumulative frequencyA running total of the number of subjects surveyed
Example:
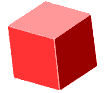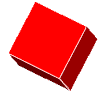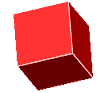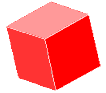
 cube
cubeA solid figure with six congruent square faces
Examples:

 cross products
cross productsTwo equal products obtained by multiplying the second term of each ratio by the first term of the other ratio in a proportion
Example:
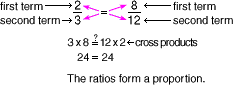 corresponding sides
corresponding sidesSides that are in the same position in different plane figures
Example:
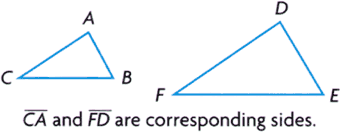 corresponding angles
corresponding anglesAngles that are in the same position in different plane figures
Example:
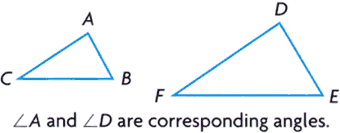 coordinates
coordinatesThe numbers in an ordered pair
Example:

(1,3) are the coordinates of A.
(
-4,
-3) are the coordinates of B.
coordinate planeA plane formed by a horizontal line (x-axis) that intersects a vertical line (y-axis)
Example:
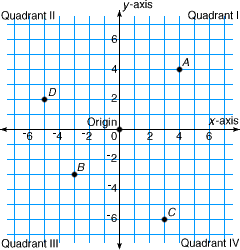 convenience sample
convenience sampleA sample of the most available subjects in the population used to obtain quick results
Example:
You could interview shoppers in the supermarket as they walk by you.
congruent polygonsPolygons that have all sides and all angles congruent
Example:
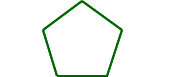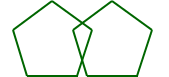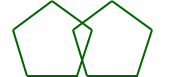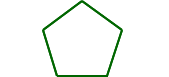
The pentagons are congruent.
congruent figuresFigures that have the same size and shape
Example:
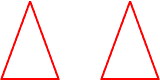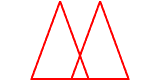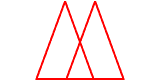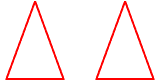
The triangles are congruent.
congruentHaving the same size and shape
Example:

The triangles are congruent.
coneA solid figure that has a circular base and one vertex
Example:
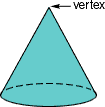 compound event
compound eventAn event made of two or more simple events
Example:

Tossing the coin and rolling the number cube are compound events.
composite numberA whole number that has more than two factors
Example:
Composite Numbers Not Composite Numbers
Number Factors Number Factors
4 1, 2, 4 1 1
6 1, 2, 3, 6 2 1, 2
8 1, 2, 4, 8 3 1, 3
9 1, 3, 9 5 1, 5
complementary anglesTwo angles whose measures have a sum of 90°
Example:
 complement
complementIn probability, the complement of an event is all outcomes different from the favorable outcome. The sum of the probability of an event and the probability of its complement is 1.
Example:

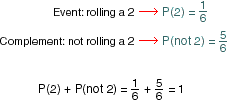 compensation
compensationA mental math strategy in which you change one addend to a multiple of ten and then adjust the other addend to keep the balance
Example:
16 + 9
(16 â€` 1) + (9 + 1)
15 + 10 = 25
compatible numbersNumbers that are easy to compute mentally when performing operations
Example:
Estimate 4,126 ÷ 8.
Think: 40 and 8 are
compatible numbers.
4,126 ÷ 8
4,1

6 ÷

4,000 ÷ 8 = 500
So, 4,126 ÷ 8 is about 500.
Commutative PropertyThe property that states that when the order of addends or factors is changed, the sum or product is the same
Examples:
9 + 4 = 4 + 9
6 x 3 = 3 x 6
common mutipleA number that is a multiple of two or more numbers
Example:
multiples of 4: 4, 8, 12, 16, 24 . . .
multiples of 6: 6, 12, 18, 24 . . . A common multiple of 4 and 6 is 24
common factorA number that is a factor of two or more numbers
Example:
factors of 6: 1, 2, 3, 6
factors of 12: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 12 The common factors of 6 and 12 are
1, 2, 3, and 6.
clusteringA method used to estimate a sum when all addends are about the same
Example:
1,802
2,182
+1,999 The three addends are
close to 2,000
3 x 2,000 = 6,000 Multiply
closed figureA figure that begins and ends at the same point
Examples:
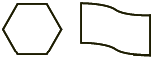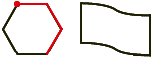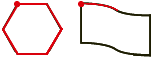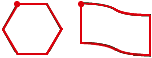 circumference
circumferenceThe distance around a circle
Example:
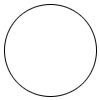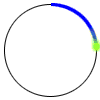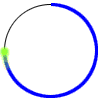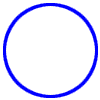 circle graph
circle graphA graph that shows how parts of the data are related to the whole and to each other
Example:
Favorite Sport
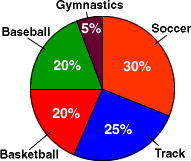 circle
circleA closed plane figure with all points of the figure the same distance from the center
Example:
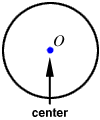 chord
chordA line segment with its endpoints on a circle
Example:
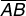
is a chord of circle O.
certainSure to happen; will always happen
center of a circleThe point inside a circle that is the same distance from each point on the circle
Example:
 Celsius
CelsiusA metric scale for measuring temperature
Example:
 capacity
capacityThe amount a container can hold when filled
Example:
 box-and-whisker graph
box-and-whisker graphA graph that shows how far apart and how evenly data are distributed
Example:
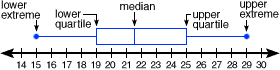 bisect
bisectTo divide into two equal parts
Example:
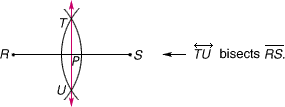 biased sample
biased sampleA sample is biased if individuals or groups from the population are not represented in the sample
biased questionA question that leads to a specific response or excludes a certain group
baseA side of a polygon or a face of a solid figure by which the figure is measured or named
Examples:
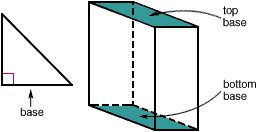 base
baseA number used as a repeated factor
Example:
8
3= 8 x 8 x 8. The base is 8.
bar graphA graph that uses horizontal or vertical bars to display countable data
Example:
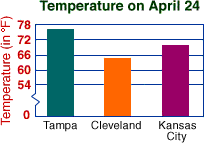 axes
axesThe horizontal number line (x-axis) and the vertical number line (y-axis) on the coordinate plane; the lines at the side and bottom of a graph
Examples:
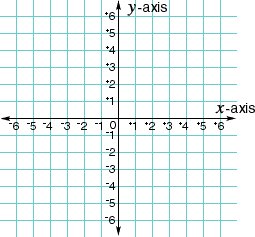
 average
averageThe number obtained by dividing the sum of a set of numbers by the number of addends; see also mean.
Example:
8.3 7.9 8.3 8.0
(8.3 + 7.9 + 8.3 + 8.0) ÷ 4 = 32.5 ÷ 4 = 8.125
The average is 8.125.
Associative PropertyThe property that states that the way addends are grouped or factors are grouped does not change the sum or the product
Examples:
12 + (5 + 9) = (12 + 5) + 9
(9 x 8) x 3 = 9 x (8 x 3)
areaThe number of square units needed to cover a surface
Example:
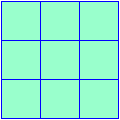
The area is 9 square units.
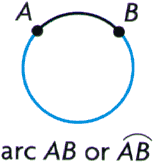
arcA part of a circle named by its endpoints
Example: