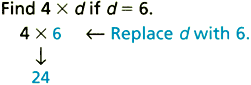Copy of `Harcourt school publishers - Math glossary`
The wordlist doesn't exist anymore, or, the website doesn't exist anymore. On this page you can find a copy of the original information. The information may have been taken offline because it is outdated.
|
|
|
Harcourt school publishers - Math glossary
Category: Mathematics and statistics
Date & country: 23/12/2007, UK
Words: 270
|
principalThe amount of money borrowed or saved
prime numberA whole number greater than 1 whose only factors are 1 and itself
Example:
Prime Not Prime
Number Factors Number Factors
2 1, 2 4 1, 2, 4
3 1, 3 6 1, 2, 3, 6
5 1, 5 9 1, 3, 9
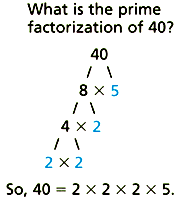
prime factorizationA number written as the product of all its prime factors
Example:
 prediction
predictionA reasonable guess as to what will happen
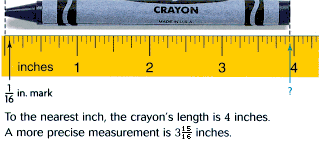
precisionA property of measurement related to the unit of measure used; the smaller the unit of measure used, the more exact the measurement is.
Example:
 positive integer
positive integerAny integer greater than zero
Example:
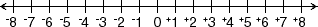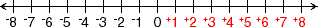 polyhedron
polyhedronA solid figure with flat faces that are polygons
Examples:
 population
populationThe entire group of objects or individuals considered for a survey
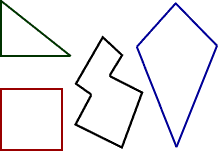
polygonA closed plane figure formed by three or more line segments
Examples:
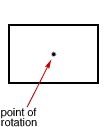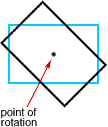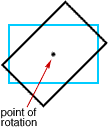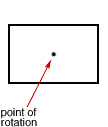
 point of rotation
point of rotationThe central point around which a figure is rotated
Example:
 point
pointAn exact location in space, usually represented by a dot
Example:
point A
plane figureA figure which lies in a plane
Examples:
 plane
planeA flat surface that extends without end in all directions
Example:
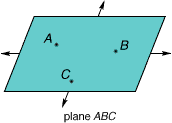
Use three points in any order that are not on a line to name the plane.
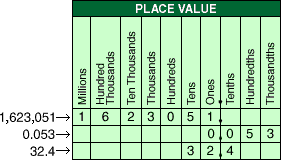
place valuePlace value determines the value of a digit in a number, based on the location of the digit.
Example:
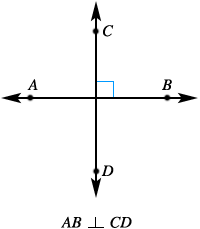
 perpendicular lines
perpendicular linesTwo lines that intersect to form four right angles
Example:
 period
periodEach group of three digits separated by commas in a multidigit number
Example:
Period Period Period
Millions Thousands Ones
Hundreds Tens Ones Hundreds Tens Ones Hundreds Tens Ones
8 5, 6 4 3, 9 0 0
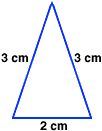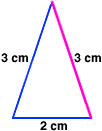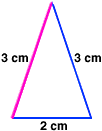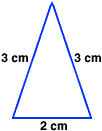
perimeterThe distance around a figure
Example:
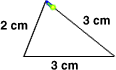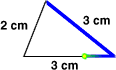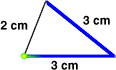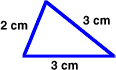
2 cm + 3 cm + 3 cm = 8 cm
The perimeter of this figure is 8 centimeters.
percentThe ratio of a number to 100; percent means 'per hundred.'
Example:
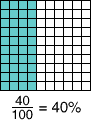
40% of the squares are shaded.
pentagonA polygon with five sides
Examples:
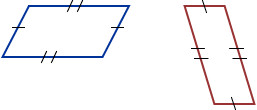
 parallelogram
parallelogramA quadrilateral whose opposite sides are parallel and congruent
Examples:
 parallel lines
parallel linesLines in a plane that never intersect
Example:

 overestimate
overestimateAn estimate that is greater than the exact answer
Example:
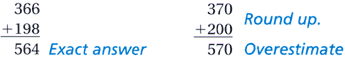 outlier
outlierA data value that stands out from others in a set; outliers can significantly affect measures of central tendency.
Example:

Free-Throw Baskets Made
outcomeA possible result of a probability experiment
Example:

Toss a coin. The outcomes are heads and tails.
originThe point where the x-axis and the y-axis in the coordinate plane intersect, (0, 0)
Example:
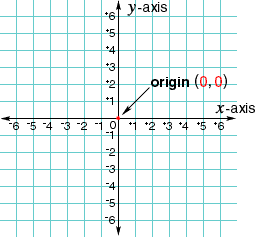 ordered pair
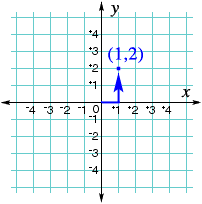
ordered pairA pair of numbers used to locate a point on a coordinate plane; the first number tells how far to move horizontally and the second number tells how far to move vertically
Example:
(1,2) represents 1 unit to the right of zero and 2 units up.
 order of operations
order of operationsThe rules for performing operations in expressions with more than one operation; first perform the operations in parentheses, clear the exponents, perform all multiplication and division, and then perform all addition and subtraction.
Examples:
10 ÷ 2 + 8 x 2
3 - 4
10 ÷ 2 + 8 x 8 - 4
5 + 64 - 4
65 Clear exponent.
Multiply and divide.
Add and subtract.
10 ÷ (2 + 8) x 2
3 - 4
10 ÷ 10 x 2
3 - 4
10 ÷ 10 x 8 - 4
8 - 4
4 Add inside parentheses.
Clear exponent.
Multiply and divide.
Subtract.
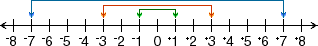
oppositesTwo numbers that are the same distance, but in opposite directions, from zero on a number line
Example:
These pairs of numbers are opposites on the number line.
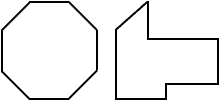
 octagon
octagonA polygon with eight sides
Examples:
 obtuse triangle
obtuse triangleA triangle that has one obtuse angle
Example:
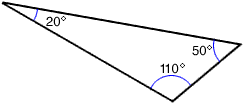 obtuse angle
obtuse angleAn angle whose measure is greater than 90° and less than 180°
Example:
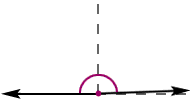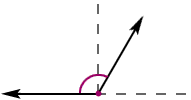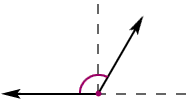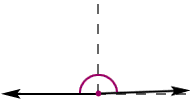 numerical expression
numerical expressionA mathematical phrase that uses only numbers and operation symbols
Examples:
60 + 25
42 ÷ 7
51 x 36
numeratorThe number above the bar in a fraction that tells how many equal parts of the whole are being considered
Example:
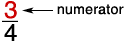 number line
number lineA line with equally spaced tick marks named by numbers
Example:
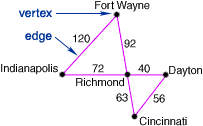
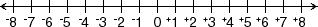 network
networkA graph with vertices and edges. In a network a vertex is a point that represents an object. The edge is a connection between vertices.
Example:
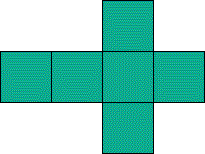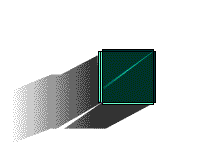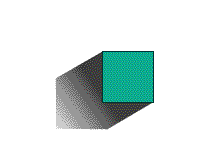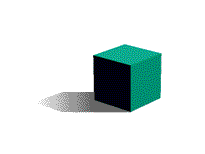
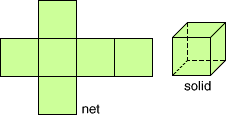
 net
netAn arrangement of two-dimensional figures that can be folded to make a polyhedron
Example:
 negative integer
negative integerAny integer less than zero
Example:
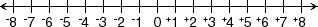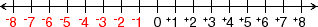 multistep problem
multistep problemA problem requiring more than one step to solve
Example:
The soccer players sold bottles of water to earn money for equipment. They charged $2.25 for each bottle of water. They sold 52 bottles on Saturday and 45 bottles on Sunday. How much did they earn?
Step 1
Add to find the total number of bottles sold.
52

bottles sold on Saturday
+45

bottles sold on Sunday
97
The players sold 97 bottles of water.
Step 2
Multiply to find the amount of money earned.
$2.25

price for each bottle
x 97

total number of bottles
$218.25
So, the players earned $218.25
Multiplication Property of EqualityThe property that states that if you multiply both sides of an equation by the same number, the sides remain equal
Example:
10 = 10
5 x 10 = 5 x 10
50 = 50
multiple-line graphA line graph that represents two or more sets of data
Example:
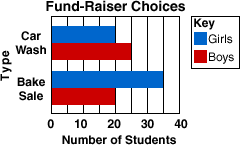
 multiple-bar graph
multiple-bar graphA bar graph that represents two or more sets of data
Example:
 multiple
multipleThe product of a given whole number and another whole number
Example:
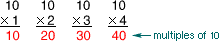 mode
modeThe numbers or items that occur most often in a set of data
Example:
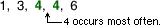
The mode of 1, 3, 4, 4, and 6 is 4.
mixed numberA number represented by a whole number and a fraction
Example:
2 1
2
midpointThe point that divides a line segment into two congruent line segments
Example:
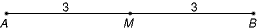

M is the midpoint of
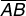
.
metric systemA measurement system that measures length in millimeters, centimeters, meters, and kilometers; capacity in liters and milliliters; mass in grams and kilograms; and temperature in degrees Celsius
medianThe middle number or the average of the two middle numbers in an ordered set of data
Example:
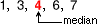
The median of 1, 3, 4, 6, and 7 is 4.
measure of central tendencyA measure used to describe data; the mean, median, and mode are measures of central tendency.
meanThe number found by dividing the sum of a set of numbers by the number of addends; see also average
Example:
74, 91, 63, 92, 85

The mean is 81.
map scaleA ratio that compares the distance on a map to the actual distance
Example:
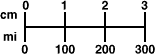
The scale is 1 cm = 100 mi.
lower quartileThe median of the lower half of a set of data
Example:
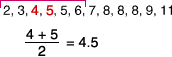
The lower quartile is 4.5.
lower extremeThe least number in a set of data
Example:
2, 3, 4, 5, 5, 6, 7, 8, 8, 8, 9, 11
The lower extreme is 2.
line symmetryA figure has line symmetry if a line can separate the figure into two congruent parts
Example:
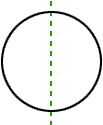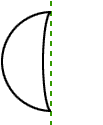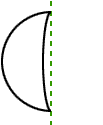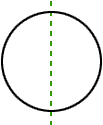 line segment
line segmentA part of a line that includes two points, called endpoints, and all of the points between them
Example:

line segment AB or line segment BA
line plotA graph that shows frequency of data along a number line
Example:
 line of symmetry
line of symmetryA line that divides a figure into two congruent parts
Example:
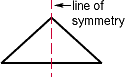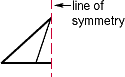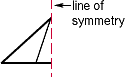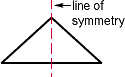 line graph
line graphA graph that uses a line to show how data change over time
Example:
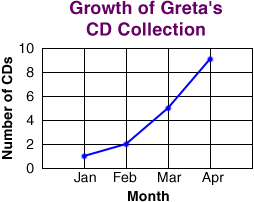 line
lineA straight path in a plane that goes on forever in opposite directions
Example:
 like terms
like termsTerms that have the same variable with the same exponent
Examples:
Algebraic Expression Like Terms
6x + 5x + 17 6x and 5x
42 + 13y
2 + 10y
2 13y
2 and 10y
2
less than (<)A symbol used to compare two numbers, with the lesser number given first
Example:
6 < 8
6 is less than 8.
legIn a right triangle, either of the two sides that form the right angle
Example:
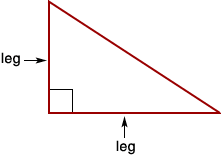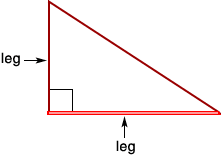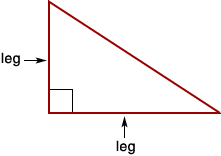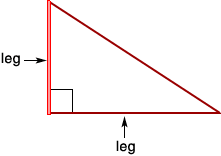 least common multiple (LCM)
least common multiple (LCM)The smallest number, other than zero, that is a common multiple of two or more numbers
Example:
multiples of 6: 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 36
multiples of 9: 9, 18, 27, 36, 45, 54
The LCM of 6 and 9 is 18.
least common denominator (LCD)The least common multiple of two or more denominators
Example:
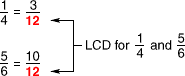 lateral faces
lateral facesThe faces in a prism or pyramid that are not bases
Example:
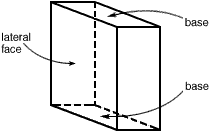
Rectangular Prism
isosceles triangleA triangle with two congruent sides
Example:
 inverse operations
inverse operationsOpposite operations that undo each other; addition and subtraction are inverse operations; multiplication and division are inverse operations
Examples:
5 + 4 = 9, so 9 â€` 4 = 5
3 x 4 = 12, so 12 ÷ 4 = 3
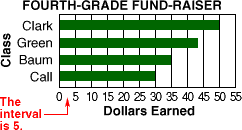
intervalThe distance between one number and the next on the scale of a graph
Example:
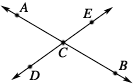
 intersecting lines
intersecting linesLines that cross at exactly one point
Example:
 integers
integersThe set of whole numbers and their opposites
Example:
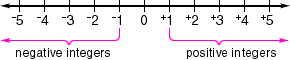 inequality
inequalityAn algebraic or numerical sentence that shows that two amounts are not equal
Examples:
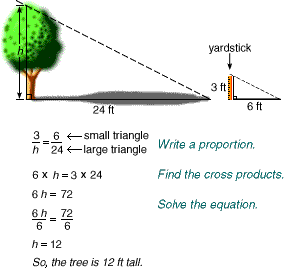
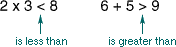 indirect measurement
indirect measurementThe technique of using similar figures and proportions to find a measure
Example:
 independent events
independent eventsEvents for which the outcome of the second event does not depend on the outcome of the first event
Example:

Tossing the coin and rolling the number cube are independent events.
impossibleNever able to happen
Identity Property of ZeroThe property that states that the sum of zero and any number is that number
Examples:
25 + 0 = 25
0 + a = a
Identity Property of OneThe property that states that the product of any number and 1 is that number
Examples:
12 x 1 = 12
1 x a = a
hypotenuseIn a right triangle, the side opposite the right angle
Example:
hypotenuse
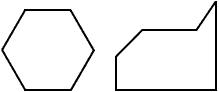
hexagonA six-sided polygon
Examples:
 histogram
histogramA bar graph that shows the number of times data occur within certain ranges or intervals
Example:
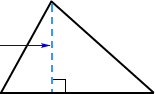
 height
heightA measure of a polygon or solid figure, taken as a perpendicular from the base of the figure
Example:
height
 greatest common factor (GCF)
greatest common factor (GCF)The greatest factor that two or more numbers have in common
Example:
18: 1, 2, 3, 6, 9, 18
30: 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 10, 15, 30
6 is the GCF of 18 and 30.
greater than (>)A symbol used to compare two numbers, with the greater number given first
Example:
8 > 6
8 is greater than 6.
Golden RectangleA rectangle with a length-to-width ratio of about 1.6 to 1
Example:
 Golden Ratio
Golden RatioA ratio equivalent to the value of about 1.6
Examples:
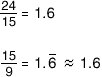 Fundamental Counting Principle
Fundamental Counting PrincipleIf one event has m possible outcomes and a second independent event has n possible outcomes, then there are m x n total possible outcomes for the two events together.
Example:
For dinner, Marsha can choose from 2 proteins (beef and fish), 4 vegetables (beans, broccoli, carrots, and corn), and 2 breads (rolls and biscuits). How many different protein-vegetable-bread selections can she make for dinner?
2 Proteins x 4 Vegetables x 2 Breads = 16
So, Marsha can choose from 16 selections.
functionA relationship between two quantities in which one quantity depends on the other
Example:
y = 5x + 4
x 0 5 10 15 20
y 4 29 54 79 104
The function table represents a function.
fractionA number that names a part of a whole or a part of a group
Example:
 frequency table
frequency tableA table that shows the total for each category or group
Example:
FREQUENCY TABLE
Day Number of Students
(Frequency)
Monday 15
Tuesday 13
Wednesday 5
Thursday 9
Friday 17
fractalA figure with repeating patterns containing shapes that are like the whole but of different sizes throughout
Example:
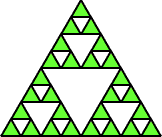 formula
formulaA rule that is expressed with symbols
Example:
formula for area of a rectangle:
Area = length x width or A = l x w
Fibonacci SequenceThe infinite sequence of numbers formed by adding two previous numbers to get the next number
Example:
1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, . . .
FahrenheitA customary scale for measuring temperature
Example:
 factor tree
factor treeA diagram that shows the prime factors of a number
Example:
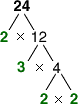
The prime factors of 24 are 2 and 3.
factorA number that is multiplied by another number to find a product
Examples:
4
4 x 7 = 28 x 7
28
The factors are 4 and 7.
faceA polygon that is a flat surface of a solid figure
Example:

face
expressionA mathematical phrase that combines operations, numbers, and/or variables
Examples:
35 â€` 15.5 3
2 ÷ a
exponentThe number that tells how many times a base is to be used as a factor
Example:
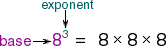
The exponent is 3, indicating that 8 is used as a factor 3 times.
eventA set of outcomes
experimental probabilityThe ratio of the number of times an event occurs to the total number of trials or times the activity is performed
Example:
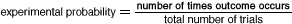 evaluate
evaluateTo find the value of a numerical or algebraic expression
Example:
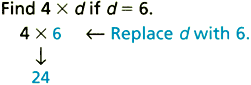 estimate
estimateA number close to an exact amount














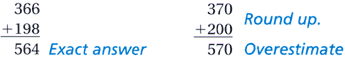


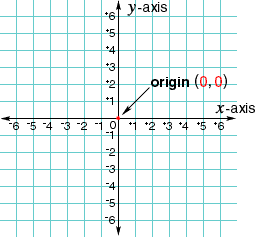










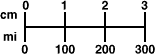
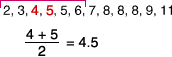





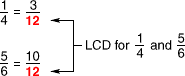




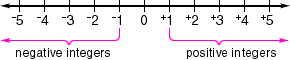


 hypotenuse
hypotenuse




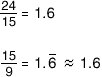
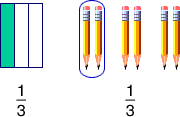


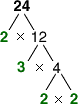
 face
face