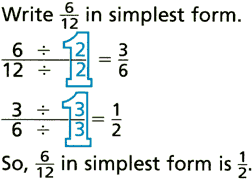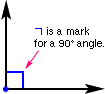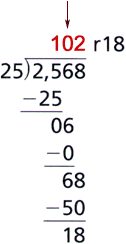Copy of `Harcourt school publishers - Math glossary`
The wordlist doesn't exist anymore, or, the website doesn't exist anymore. On this page you can find a copy of the original information. The information may have been taken offline because it is outdated.
|
|
|
Harcourt school publishers - Math glossary
Category: Mathematics and statistics
Date & country: 23/12/2007, UK
Words: 270
|
algebraic operating system (AOS)The set of procedures some calculators use to follow the order of operations
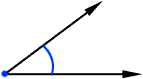
angleA figure formed by two rays that have a common endpoint
Example:
 algebraic expression
algebraic expressionAn expression that includes at least one variable
Examples:
x + 5
4n ÷ 6
adjacent anglesAngles that are side by side and have a common vertex and ray
Example:
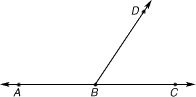

ABD is adjacent to

DBC.
additive inverseThe opposite of a given number
Examples:
1 and
-1
-27 and 27
Addition Property of EqualityThe property that states that if you add the same number to both sides of an equation, the sides remain equal
Example:
5 = 5
5 + 2 = 5 + 2
7 = 7
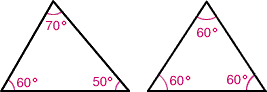
acute triangleA triangle in which all three angles are acute
Examples:
 acute angle
acute angleAn angle that has a measure greater than 0° and less than 90°
Example:
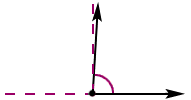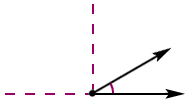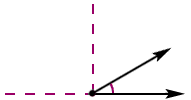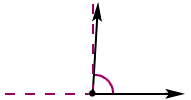 absolute value
absolute valueThe distance of a number from zero on a number line
Example:
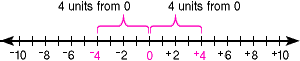 -
-4

The absolute value of
-4 is 4.
+4

The absolute value of
+4 is 4.
y-coordinateThe second number in an ordered pair it tells the distance to move up or down from (0,0)
Example:
 y-axis
y-axisThe vertical number line on a coordinate plane
Example:
 x-coordinate
x-coordinateThe first number in an ordered pair which tells the distance to move right or left from (0, 0)
Example:
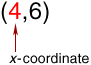 x-axis
x-axisThe horizontal number line on a coordinate plane
Example:
 whole number
whole numberOne of the numbers 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, . . . The set of whole numbers goes on without end.
volumeThe measure of the amount of space a solid figure occupies
Example:
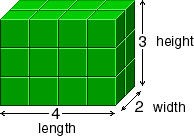
The volume of this figure is 24 cubic units
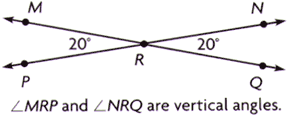
vertical anglesA pair of opposite congruent angles formed where two lines intersect
Example:
 vertex
vertexThe point where two or more rays meet; the point of intersection of two sides of a polygon; the point of intersection of three or more edges of a solid figure; the top point of a cone; the plural of vertex is vertices
Examples:
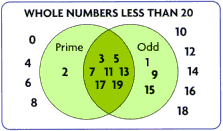
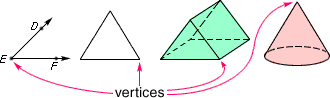 Venn diagram
Venn diagramA diagram that shows relationships among sets of things
Example:
 variable
variableA letter or symbol that stands for one or more numbers
Example:
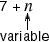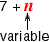 upper quartile
upper quartileThe median of the upper half of a set of data
Example:
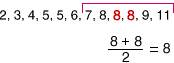
The upper quartile is 8.
upper extremeThe greatest number in a set of data
Example:
2, 3, 4, 5, 5, 6, 7, 8, 8, 8, 9, 11
The upper extreme is 11.
unlike fractionsFractions with different denominators
Example:
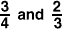
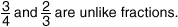 unit rate
unit rateA rate that has 1 unit as its second term
Example:
$1.45 per pound
underestimateAn estimate that is less than the exact answer
Example:
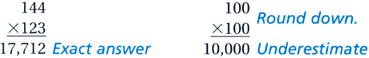 unbiased sample
unbiased sampleA sample is unbiased if every individual in the population has an equal chance of being selected
triangular numberA number that can be represented by a triangular array
Examples:
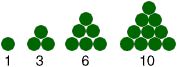 triangle
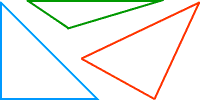
triangleA polygon with three sides
Examples:
 tree diagram
tree diagramA diagram that shows all possible outcomes for an event
Example:

So, there are 6 possible outcomes.
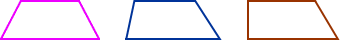
trapezoidA quadrilateral with one pair of parallel sides
Examples:
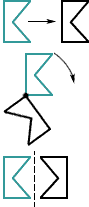
 translation (slide)
translation (slide)A movement of a figure along a straight line
Example:
 transformation
transformationThe moving of a figure by a translation, reflection, or rotation
Examples:
translation
rotation
reflection
 three-dimensional
three-dimensionalMeasured in three directions, such as length, width, and height
Example:
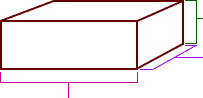
height
width
length
theoretical probabilityA comparison of the number of favorable outcomes to the number of possible equally likely outcomes
Example:
 tessellation
tessellationAn arrangement of closed figures that completely covers a surface with no gaps and no overlaps
Example:
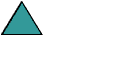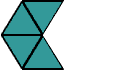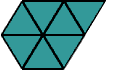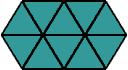 terms
termsThe parts of an expression that are separated by an addition or subtraction sign
Example:
3x + 2y + 17
3x, 2y, and 17 are terms in the expression.
terminating decimalA decimal that ends, having a finite number of digits after the decimal point
Examples:
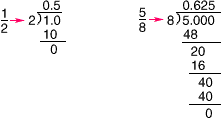
0.5 and 0.625 are terminating decimals.
termEach of the numbers in a sequence
Example:
3, 6, 12, 24
6 is a term in the sequence.
termOne of the numbers in a ratio
Example:
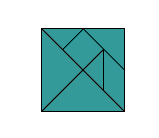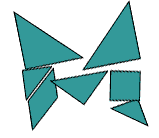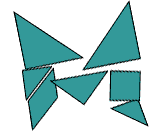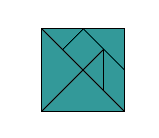
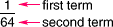 tangram
tangramA puzzle consisting of seven polygon-shaped pieces that can be rearranged to make various figures or shapes
Example:
 tally table
tally tableA table with categories for recording each piece of data with tally marks as it is collected
Example:
 systematic sample
systematic sampleA sampling method in which one subject is selected at random and subsequent subjects are selected according to a pattern
Example:
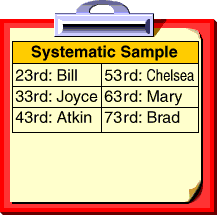 survey
surveyA method of gathering information about a group
surface areaThe sum of the areas of all the faces, or surfaces, of a solid figure
Example:
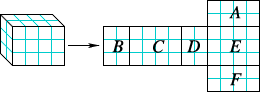
Surface Area = A + B + C + D + E + F
= 8 + 6 + 12 + 6 + 12 + 8 = 52, or 52 units
2
supplementary anglesTwo angles whose measures have a sum of 180°
Example:
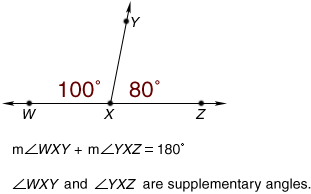 sum
sumThe answer to an addition problem
Example:
12 + 7 = 19
The sum is 19.
Subtraction Property of EqualityThe property that states that if you subtract the same number from both sides of an equation, the sides remain equal
Example:
5 = 5
5 â€` 2 = 5 â€` 2
3 = 3
straight angleAn angle whose measure is 180°
Example:


XYZ is a straight angle.
stem-and-leaf plotA data display that shows groups of data arranged by place value
Example:

This plot shows the number of sit-ups a group of students did in one minute.
standard formA way to write numbers using the digits 0-9
Example:
3,027
square rootOne of two equal factors of a number
Example:
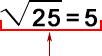
because 5
2 = 5 x 5 = 25.
Read: The square root of twenty-five equals five.
square numberThe product of a number and itself; a number with the exponent 2
Example:
Read 3
2 as '3 squared.'
3
2 = 3 x 3 = 9 So, 3
2 = 9.
8
2 = 8 x 8 = 64 So, 8
2 = 64.
squareA rectangle with 4 equal sides
Example:
26 in.
26 in.

26 in.
26 in.
sphereA solid figure that has the shape of a round ball; all points are the same distance from the center
Example:
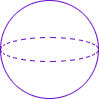
 solve an equation
solve an equationTo find the value of a variable that makes an equation true
Example:
c - 12 = 17 Write the equation.
c - 12 + 12 = 17 + 12 Add 12 to each side.
c = 29
solutionA value that, when substituted for a variable in an equation, makes the equation true
Example:
x + 4 = 7
Since 3 + 4 = 7, then x = 3.
So, 3 is the solution.
solid figureA three-dimensional figure
Examples:
sphere
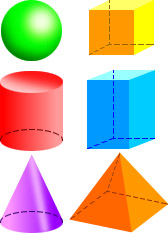
cube
cylinder
rectangular
prism
cone
square
pyramid
simulationA model of an experiment that would be too difficult or too time-consuming to actually perform
simplest formA fraction is in simplest form when the numerator and denominator have only 1 as their common factor
Example:
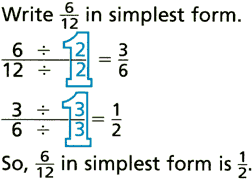 simple interest
simple interestA fixed percent of the principal, paid yearly
Example:
Carol invested $150 at a simple interest rate of 4%. Find the interest she will earn in 1 year.
I = prt
I = 150 x 4% x 1 p = $150, r = 4%, t = 1 year
I = 150 x 0.04 x 1 Multiply.
I = 6 So, the interest earned in 1 year is $6.
similar figuresFigures with the same shape but not necessarily the same size
Example:
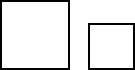
The two figures are similar.
sequenceAn ordered set of numbers
Example:
1, 5, 9, 13, . . .
self similarityA figure has self-similarity if it contains a repeating pattern of smaller and smaller parts that are like the whole, but different in size
Example:
 sector
sectorA region enclosed by two radii and the arc joining their endpoints
Example:
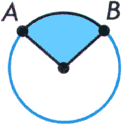 scatterplot
scatterplotA graph with points plotted to show a relationship between two variables
Example:
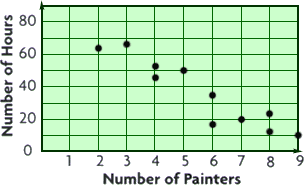 scalene triangle
scalene triangleA triangle with no congruent sides
Example:
 scale drawing
scale drawingA drawing that shows a real object smaller than (a reduction) or larger than (an enlargement) the real object
Example:
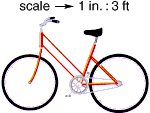 scale
scaleThe ratio between two sets of measurements
Example:
scale 1 cm : 2 m
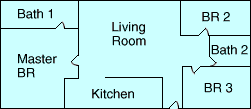 scale
scaleOn a graph, the numbers placed at fixed distances to help label the graph
Example:
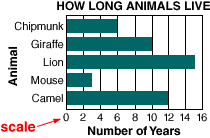 sales tax
sales taxA percent of the cost of an item, added onto the item's cost
sampleA part of a population
sample spaceThe set of all possible outcomes
Example:

The sample space is 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6.
rotational symmetryThe property of a figure that can be rotated less than 360° around a central point and still be congruent to the original figure
Example:
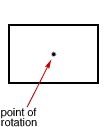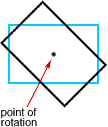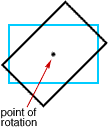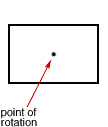 rotation (turn)
rotation (turn)A movement of a figure by turning it around a fixed point
Example:
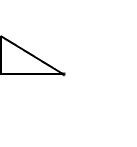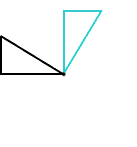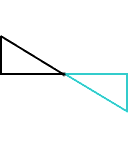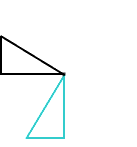 right triangle
right triangleA triangle with one right angle
Examples:
 right angle
right angleAn angle formed by perpendicular lines, line segments, or rays and with a measure of 90°
Example:
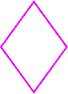
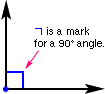 rhombus
rhombusA parallelogram with four congruent sides
Example:
 relation
relationA set of ordered pairs
Example:
(5,1) (10,2) (15,3) (20,4) (25,5)
repeating decimalA decimal that doesn't end; it shows a repeating pattern of digits after the decimal point.
Examples:
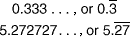 regular polygon
regular polygonA polygon in which all sides are congruent and all angles are congruent
Examples:
 reflection (flip)
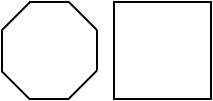
reflection (flip)A movement of a figure to a new position by flipping it over a line
Example:
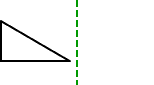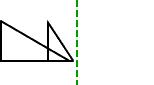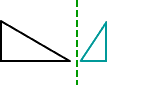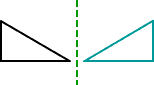 rectangular prism
rectangular prismA solid figure in which all six faces are rectangles
Example:
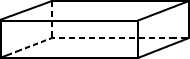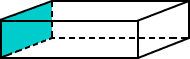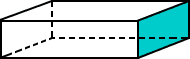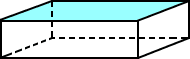 rectangle
rectangleA parallelogram with four right angles
Example:
 reciprocal
reciprocalOne of two numbers whose product is 1; two numbers are reciprocals of each other if their product equals 1.
Example:
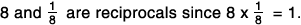 ray
rayA part of a line, with one endpoint, that continues without end in one direction
Example:
 rational number
rational numberAny number that can be written as a ratio
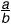
where a and b are integers and b

0
Examples:
0.5
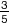 -
-3 8
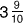 rate
rateA ratio that compares two quantities having different units of measure
Example:
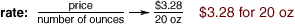 ratio
ratioThe comparison of two numbers by division
Example:

Compare: Ratio: Type of Ratio:
red counters to all counters 2 to 5 part to whole
all counters to red counters 5 to 2 whole to part
red counters to yellow counters 2 to 3 part to part
rangeThe difference between the greatest and least numbers in a set of data
Example:
Month Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov
Temperature 82°F 83°F 83°F 82°F 82°F 80°F
random sampleA sample in which each individual or object in the population has an equal chance of being selected
radiusA line segment with one endpoint at the center of a circle and the other endpoint on the circle
Example:
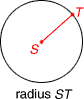 quotient
quotientThe number, not including the remainder, that results from dividing
Example:
quotient
 quadrilateral
quadrilateralA polygon with four sides
Examples:
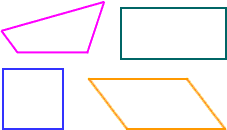 quadrants
quadrantsThe four regions of the coordinate plane
Example:
 Pythagorean Theorem
Pythagorean TheoremIn any right triangle, if a and b are the lengths of the legs and c is the length of the hypotenuse, then a
2 + b
2 = c
2 Example:
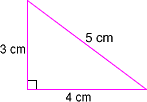
a
2 + b
2 = c
2 Replace the variables
with the known lengths.
3
2 + 4
2 = 5
2 9 + 16 = 25
25 = 25
pyramidA solid figure with a polygon base and all other faces triangles that meet at a common vertex
Examples:
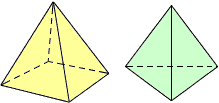
rectangular pyramid triangular pyramid
proportionAn equation that shows that two ratios are equal
Example:
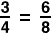 product
productThe answer to a multiplication problem
Example:
6
6 x 2 = 12 x 2
12
The product is 12.
Property of ZeroThe property that states that the product of any number and zero is zero
Examples:
8 x 0 = 0
0 x a = 0
probability (P)The chance that an event will occur expressed as the ratio of the number of favorable outcomes to the number of possible outcomes
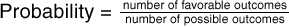 prism
prismA solid figure that has two congruent, polygon-shaped bases, and other faces that are all rectangles
Examples:
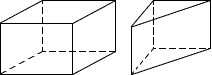
rectangular prism triangular prism




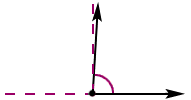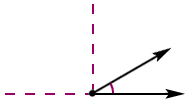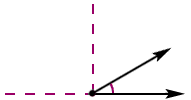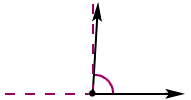



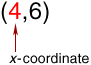





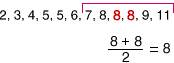
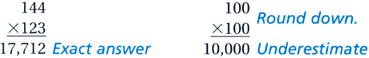






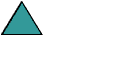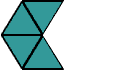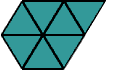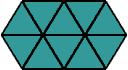
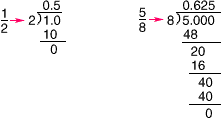






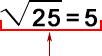 because 52 = 5 x 5 = 25.
because 52 = 5 x 5 = 25.  26 in.
26 in.